
As advanced machine learning algorithms are gaining acceptance across many organizations and domains, machine learning interpretability is growing in importance to help extract insight and clarity regarding how these algorithms are performing and why one prediction is made over another. There are many methodologies to interpret machine learning results (i.e. variable importance via permutation, partial dependence plots, local interpretable model-agnostic explanations), and many machine learning R packages implement their own versions of one or more methodologies. However, some recent R packages that focus purely on ML interpretability agnostic to any specific ML algorithm are gaining popularity. One such package is DALEX and this post covers what this package does (and does not do) so that you can determine if it should become part of your preferred machine learning toolbox.
DALEX is an R package with a set of tools that help to provide Descriptive mAchine Learning EXplanations ranging from global to local interpretability methods. In particular, it makes comparing performance across multiple models convenient. However, as is, there are some problems with this package scaling to wider data sets commonly used by organizations. The following provides a quick list of its pros and cons:
Advantages
pdp package.Disadvantages
I leverage the following packages:
# load required packages
library(rsample)
library(dplyr)
library(h2o)
library(DALEX)
# initialize h2o session
h2o.no_progress()
h2o.init()
## Connection successful!
##
## R is connected to the H2O cluster:
## H2O cluster uptime: 4 hours 30 minutes
## H2O cluster timezone: America/New_York
## H2O data parsing timezone: UTC
## H2O cluster version: 3.18.0.11
## H2O cluster version age: 1 month and 17 days
## H2O cluster name: H2O_started_from_R_bradboehmke_gny210
## H2O cluster total nodes: 1
## H2O cluster total memory: 1.01 GB
## H2O cluster total cores: 4
## H2O cluster allowed cores: 4
## H2O cluster healthy: TRUE
## H2O Connection ip: localhost
## H2O Connection port: 54321
## H2O Connection proxy: NA
## H2O Internal Security: FALSE
## H2O API Extensions: XGBoost, Algos, AutoML, Core V3, Core V4
## R Version: R version 3.5.0 (2018-04-23)
To demonstrate model visualization techniques we’ll use the employee attrition data that has been included in the rsample package. This demonstrates a binary classification problem (“Yes” vs. “No”) but the same process that you’ll observe can be used for a regression problem.
To demonstrate DALEX’s capabilities we’ll use the employee attrition data that has been included in the rsample package. This demonstrates a binary classification problem (“Yes” vs. “No”) but the same process that you’ll observe can be used for a regression problem.
I perform a few house cleaning tasks on the data prior to converting to an h2o object and splitting.
NOTE: To use some of DALEX’s functions, categorical predictor variables need to be converted to factors. Also, I force ordered factors to be unordered as h2o does not support ordered categorical variables.
# classification data
df <- rsample::attrition %>%
mutate_if(is.ordered, factor, ordered = FALSE) %>%
mutate(Attrition = recode(Attrition, "Yes" = "1", "No" = "0") %>% factor(levels = c("1", "0")))
# convert to h2o object
df.h2o <- as.h2o(df)
# create train, validation, and test splits
set.seed(123)
splits <- h2o.splitFrame(df.h2o, ratios = c(.7, .15), destination_frames = c("train","valid","test"))
names(splits) <- c("train","valid","test")
# variable names for resonse & features
y <- "Attrition"
x <- setdiff(names(df), y)
We will explore how to visualize a few of the more common machine learning algorithms implemented with h2o. For brevity I train default models and do not emphasize hyperparameter tuning. The following produces a regularized logistic regression, random forest, and gradient boosting machine models; all of which provide AUCs ranging between .75-.79. Although these models have distinct AUC scores, our objective is to understand how these models come to this conclusion in similar or different ways based on underlying logic and data structure.
# elastic net model
glm <- h2o.glm(
x = x,
y = y,
training_frame = splits$train,
validation_frame = splits$valid,
family = "binomial",
seed = 123
)
# random forest model
rf <- h2o.randomForest(
x = x,
y = y,
training_frame = splits$train,
validation_frame = splits$valid,
ntrees = 1000,
stopping_metric = "AUC",
stopping_rounds = 10,
stopping_tolerance = 0.005,
seed = 123
)
# gradient boosting machine model
gbm <- h2o.gbm(
x = x,
y = y,
training_frame = splits$train,
validation_frame = splits$valid,
ntrees = 1000,
stopping_metric = "AUC",
stopping_rounds = 10,
stopping_tolerance = 0.005,
seed = 123
)
# model performance
h2o.auc(glm, valid = TRUE)
## [1] 0.7870935
h2o.auc(rf, valid = TRUE)
## [1] 0.7681021
h2o.auc(gbm, valid = TRUE)
## [1] 0.7468242
The DALEX architecture can be split into three primary operations:
DALEX::explain(), which is just a list that contains the training data and meta data on the machine learning model.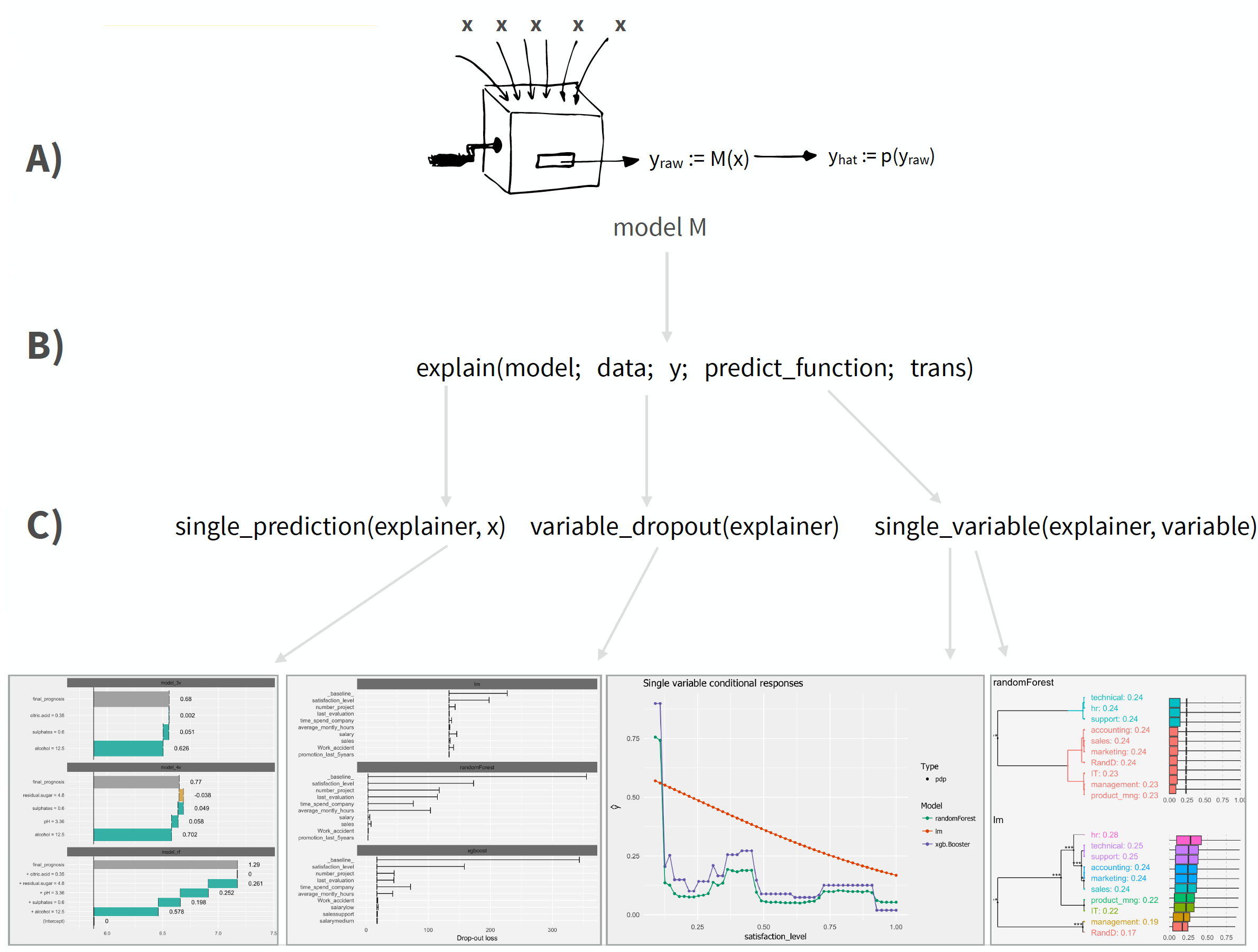
Although DALEX does have native support for some ML model objects (i.e. lm, randomForest), it does not have native many of the preferred ML packages produced more recently (i.e. h2o, xgboost, ranger). To make DALEX compatible with these objects, we need three things:
x_valid: Our feature set needs to be in its original form not as an h2o object.y_valid: Our response variable needs to be a numeric vector. For regression problems this is simple, as it will already be in this format. For binary classification this requires you to convert the responses to 0/1.pred: a custom predict function that returns a vector of numeric values. For binary classification problems, this means extracting the probability of the response.# convert feature data to non-h2o objects
x_valid <- as.data.frame(splits$valid)[, x]
# make response variable numeric binary vector
y_valid <- as.vector(as.numeric(as.character(splits$valid$Attrition)))
head(y_valid)
## [1] 0 0 0 0 0 0
# create custom predict function
pred <- function(model, newdata) {
results <- as.data.frame(h2o.predict(model, as.h2o(newdata)))
return(results[[3L]])
}
pred(rf, x_valid) %>% head()
## [1] 0.18181818 0.27272727 0.06060606 0.54545455 0.03030303 0.42424242
Once you have these three components, you can now create your explainer objects for each ML model. Considering I used a validation set to compute the AUC, we want to use that same validation set for ML interpretability.
# elastic net explainer
explainer_glm <- explain(
model = glm,
data = x_valid,
y = y_valid,
predict_function = pred,
label = "h2o glm"
)
# random forest explainer
explainer_rf <- explain(
model = rf,
data = x_valid,
y = y_valid,
predict_function = pred,
label = "h2o rf"
)
# GBM explainer
explainer_gbm <- explain(
model = gbm,
data = x_valid,
y = y_valid,
predict_function = pred,
label = "h2o gbm"
)
# example of explainer object
class(explainer_glm)
## [1] "explainer"
summary(explainer_glm)
## Length Class Mode
## model 1 H2OBinomialModel S4
## data 30 data.frame list
## y 233 -none- numeric
## predict_function 1 -none- function
## link 1 -none- function
## class 1 -none- character
## label 1 -none- character
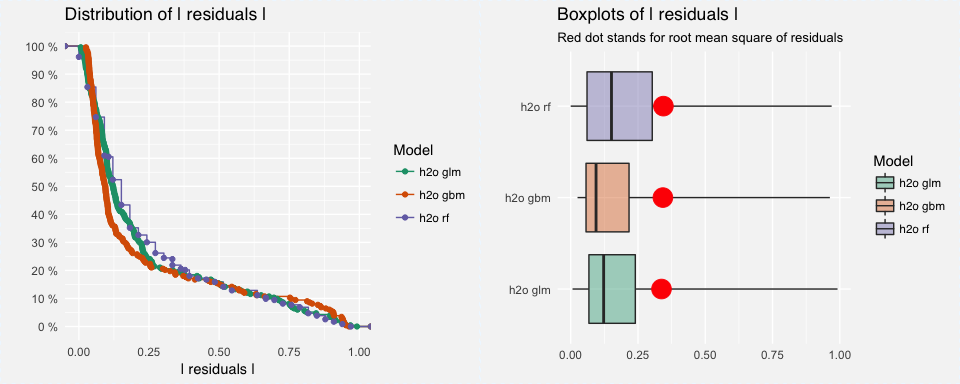
As we saw earlier, the GLM model had the highest AUC followed by the random forest model then GBM. However, a single accuracy metric can be a poor indicator of performance. Assessing residuals of predicted versus actuals can allow you to identify where models deviate in their predictive accuracy. We can use DALEX::model_performance to compute the predictions and residuals. Printing the output returns residual quantiles and plotting the output allows for easy comparison of absolute residual values across models.
In this example, the residuals are comparing the probability of attrition to the binary attrition value (1-yes, 0-no). Looking at the quantiles you can see that the median residuals are lowest for the GBM model. And looking at the boxplots you can see that the GBM model also had the lowest median absolute residual value. Thus, although the GBM model had the lowest AUC score, it actually performs best when considering the median absoluate residuals. However, you can also see a higher number of residuals in the tail of the GBM residual distribution (left plot) suggesting that there may be a higher number of large residuals compared to the GLM model. This helps to illustrate how your residuals behave similarly and differently across models.
# compute predictions & residuals
resids_glm <- model_performance(explainer_glm)
resids_rf <- model_performance(explainer_rf)
resids_gbm <- model_performance(explainer_gbm)
# assess quantiles for residuals
resids_glm
## 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
## -0.99155845 -0.70432615 0.01281214 0.03402030 0.06143281 0.08362550
## 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
## 0.10051641 0.12637877 0.17583980 0.22675709 0.47507569
resids_rf
## 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
## -0.96969697 -0.66666667 0.00000000 0.03030303 0.06060606 0.09090909
## 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
## 0.12121212 0.15151515 0.18181818 0.27272727 0.66666667
resids_gbm
## 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
## -0.96307337 -0.75623698 0.03258538 0.04195091 0.05344621 0.06382511
## 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
## 0.07845749 0.09643740 0.11312648 0.18169305 0.66208105
# create comparison plot of residuals for each model
p1 <- plot(resids_glm, resids_rf, resids_gbm)
p2 <- plot(resids_glm, resids_rf, resids_gbm, geom = "boxplot")
gridExtra::grid.arrange(p1, p2, nrow = 1)
An important task in ML interpretation is to understand which predictor variables are relatively influential on the predicted outcome. Many ML algorithms have their own unique ways to quantify the importance or relative influence of each feature (i.e. coefficients for linear models, impurity for tree-based models). However, other algorithms like naive Bayes classifiers and support vector machines do not. This makes it difficult to compare variable importance across multiple models.
DALEX uses a model agnostic variable importance measure computed via permutation. This approach follows the following steps:
For any given loss function do
1: compute loss function for full model (denote _full_model_)
2: randomize response variable, apply given ML, and compute loss function (denote _baseline_)
3: for variable j
| randomize values
| apply given ML model
| compute & record loss function
end
To compute the permuted variable importance we use DALEX::variable_importance(). The printed output just provides a data frame with the output and plotting the three variable importance objects allows us to compare the most influential variables for each model. How do we interpret this plot?
_full_model_. The default loss function is squared error but any custom loss function can be supplied._baseline_. This value represents the loss function when our response values are randomized and should be a good indication of the worst-possible loss function value when there is no predictive signal in the data.The results provide some interesting insights. First, the shifted x-axis left edge helps to illustrate the difference in the RMSE loss between the three models (i.e. GLM model has the lowest RMSE suggesting that the greater number of tail residuals in the GBM model is likely penalizing the RMSE score. Second, we can see which variables are consistently influential across all models (i.e. OverTime, EnvironmentSatisfaction, Age), variables that are influential in two but not all three (i.e. BusinessTravel, WorkLifeBalance), and variables which are only influential in one model but not others (i.e. DailyRate, YearsInCurrentRole). This helps you to see if models are picking up unique structure in the data or if they are using common logic.
In this example, all three models appear to be largely influenced by the OverTime, EnvironmentSatisfaction, Age, TotalWorkingYears, and JobLevel variables. This gives us confidences that these features have strong predictive signals.
TIP: You can incorporate custom loss functions using the loss_function argument.
# compute permutation-based variable importance
vip_glm <- variable_importance(explainer_glm, n_sample = -1, loss_function = loss_root_mean_square)
vip_rf <- variable_importance(explainer_rf, n_sample = -1, loss_function = loss_root_mean_square)
vip_gbm <- variable_importance(explainer_gbm, n_sample = -1, loss_function = loss_root_mean_square)
plot(vip_glm, vip_rf, vip_gbm, max_vars = 10)

One downfall of the permutation-based approach to variable importance is it can become slow. Since the algorithm loops through and applies a model for each predictor variable, the more features in your model the longer it will take. For this example, which includes 30 features, it takes 81 seconds to compute variable importance for all three models. However, when tested on a data set with 100 predictors it took nearly 5 minutes to compute.
TIP: variable_importance includes an n_sample argument that, by default, will sample only 1000 observations to try increase the speed of computation. Adjusting n_sample = -1 as I did in the above code chunk just means to use all observations.
# time to compute importance scores
system.time({
vip_glm <- variable_importance(explainer_glm)
vip_rf <- variable_importance(explainer_rf)
vip_gbm <- variable_importance(explainer_gbm)
})
## user system elapsed
## 34.078 1.163 81.124
Once we’ve identified influential variables across all three models, next we likely want to understand how the relationship between these influential variables and the predicted response differ between the models. This helps to indicate if each model is responding to the predictor signal similarly or if one or more models respond differently. For example, we saw that the Age variable was one of the most influential variables across all three models. The below partial dependence plot illustrates that the GBM and random forest models are using the Age signal in a similar non-linear manner; however, the GLM model is not able to capture this same non-linear relationship. So although the GLM model may perform better (re: AUC score), it may be using features in biased or misleading ways.
# compute PDP for a given variable --> uses the pdp package
pdp_glm <- variable_response(explainer_glm, variable = "Age", type = "pdp")
pdp_rf <- variable_response(explainer_rf, variable = "Age", type = "pdp")
pdp_gbm <- variable_response(explainer_gbm, variable = "Age", type = "pdp")
plot(pdp_glm, pdp_rf, pdp_gbm)

Although you can use PDPs for categorical predictor variables, DALEX provides merging path plots originally provided by the factoMerger package. For example, the EnvironmentSatisfaction variable captures the level of satisfaction regarding the working environment among employees. This variable showed up in all three models’ top 10 most influential variable lists. We can use type = "factor" to create a merging path plot and it shows very similar results for each model. Those employees that have low level of satisfaction have, on average, higher probabilities of attrition. Whereas, employees with medium to very high have about the same likelihood of attriting. The left side of the plot is the merging path plot, which shows the similarity between groups via hierarchical clustering. It illustrates that employees with medium and high satisfaction are most similar, then these employees are next most similar to employees with very high satisfaction. Then finally, the least similar group is the low satisfaction employees.
cat_glm <- variable_response(explainer_glm, variable = "EnvironmentSatisfaction", type = "factor")
cat_rf <- variable_response(explainer_rf, variable = "EnvironmentSatisfaction", type = "factor")
cat_gbm <- variable_response(explainer_gbm, variable = "EnvironmentSatisfaction", type = "factor")
plot(cat_glm, cat_rf, cat_gbm)

The previous plots help us to understand our model from a global perspective by illustrating errors, identifying the variables with the largest overall impact, and understanding predictor-response relationships across all observations. However, often, we also need to perform local interpretation which allows us to understand why a particular prediction was made for an observation. Understanding and comparing how a model uses the predictor variables to make a given prediction can provide trust to you (the analyst) and also the stakeholder(s) that will be using the model output for decision making purposes.
Although LIME and SHAP (1, 2) values have recently become popular for local ML interpretation, DALEX uses a process called break down to compute localized variable importance scores.
There are two break down approaches that can be applied. The default is called step up and the algorithm performs the following steps:
existing_data = validation data set used in explainer
new_ob = single observation to perform local interpretation on
p = number of predictors
l = list of predictors
baseline = mean predicted response of existing_data
for variable i in {1,...,p} do
for variable j in {1,...,l} do
| substitue variable j in existing_data with variable j value in new_ob
| predicted_j = mean predicted response of altered existing_data
| diff_j = absolute difference between baseline - predicted
| reset existing_data
end
| t = variable j with largest diff value
| contribution for variable t = diff value for variable t
| remove variable t from l
end
This is called step up because, essentially, it sweeps through each column, identifies the column with the largest difference score, adds that variable to the list as the most important, sweeps through the remaining columns, identifies the column with the largest score, adds that variable to the list as second most important, etc. until all variables have been assessed.
An alternative approach is called the step down which follows a similar algorithm but rather than remove the variable with the largest difference score on each sweep, it removes the variable with the smallest difference score. Both approaches are analogous to backward stepwise selection where step up removes variables with largest impact and step down removes variables with smallest impact.
To perform the break down algorithm on a single observation, use the DALEX::prediction_breakdown function. The output is a data frame with class “prediction_breakdown_explainer” that lists the contribution for each variable.
TIP: The default approach is step up but you can perform step down by adding the following argument direction = "down".
# create a single observation
new_cust <- splits$valid[1, ] %>% as.data.frame()
# compute breakdown distances
new_cust_glm <- prediction_breakdown(explainer_glm, observation = new_cust)
new_cust_rf <- prediction_breakdown(explainer_rf, observation = new_cust)
new_cust_gbm <- prediction_breakdown(explainer_gbm, observation = new_cust)
# class of prediction_breakdown output
class(new_cust_gbm)
## [1] "prediction_breakdown_explainer" "data.frame"
# check out the top 10 influential variables for this observation
new_cust_gbm[1:10, 1:5]
## variable contribution
## 1 (Intercept) 0.0000000000
## JobRole + JobRole = Laboratory_Technician 0.0377083508
## StockOptionLevel + StockOptionLevel = 0 0.0243714089
## MaritalStatus + MaritalStatus = Single 0.0242334088
## JobLevel + JobLevel = 1 0.0318770608
## Age + Age = 32 0.0261924164
## BusinessTravel + BusinessTravel = Travel_Frequently 0.0210465713
## RelationshipSatisfaction + RelationshipSatisfaction = High 0.0108111555
## Education + Education = College 0.0016911550
## PercentSalaryHike + PercentSalaryHike = 13 0.0001157596
## variable_name variable_value
## 1 Intercept 1
## JobRole JobRole Laboratory_Technician
## StockOptionLevel StockOptionLevel 0
## MaritalStatus MaritalStatus Single
## JobLevel JobLevel 1
## Age Age 32
## BusinessTravel BusinessTravel Travel_Frequently
## RelationshipSatisfaction RelationshipSatisfaction High
## Education Education College
## PercentSalaryHike PercentSalaryHike 13
## cummulative
## 1 0.00000000
## JobRole 0.03770835
## StockOptionLevel 0.06207976
## MaritalStatus 0.08631317
## JobLevel 0.11819023
## Age 0.14438265
## BusinessTravel 0.16542922
## RelationshipSatisfaction 0.17624037
## Education 0.17793153
## PercentSalaryHike 0.17804729
We can plot the entire list of contributions for each variable of a particular model. We can see that several predictors have zero contribution, while others have positive and negative contributions. For the GBM model, the predicted value for this individual observation was positively influenced (increased probability of attrition) by variables such as JobRole, StockOptionLevel, and MaritalStatus. Alternatively, variables such as JobSatisfaction, OverTime, and EnvironmentSatisfaction reduced this observations probability of attriting.
plot(new_cust_gbm)

For data sets with a small number of predictors, you can compare across multiple models in a similar way as with earlier plotting (plot(new_cust_glm, new_cust_rf, new_cust_gbm)). However, with wider data sets, this becomes cluttered and difficult to interpret. Alternatively, you can filter for the largest absolute contribution values. This causes the output class to lose its prediction_breakdown_explainer class so we can plot the results with ggplot.
Each model has a similar prediction that the new observation has a low probability of predicting:
However, how each model comes to that conclusion in a slightly different way. However, there are several predictors that we see consistently having a positive or negative impact on this observations’ probability of attriting (i.e. OverTime, EnvironmentSatisfaction, JobSatisfaction are reducing this employees probability of attriting while JobLevel, MaritalStatus, StockOptionLevel, and JobLevel are all increasing the probability of attriting). Consequently, we can have a decent amount of trust that these are strong signals for this observation regardless of model. However, when each model picks up unique signals in variables that the other models do not capture (i.e. DistanceFromHome, NumCompaniesWorked), its important to be careful how we communicate these signals to stakeholders. Since these variables do not provide consistent signals across all models we should use domain experts or other sources to help validate whether or not these predictors are trustworthy. This will help us understand if the model is using proper logic that translates well to business decisions.
library(ggplot2)
# filter for top 10 influential variables for each model and plot
list(new_cust_glm, new_cust_rf, new_cust_gbm) %>%
purrr::map(~ top_n(., 11, wt = abs(contribution))) %>%
do.call(rbind, .) %>%
mutate(variable = paste0(variable, " (", label, ")")) %>%
ggplot(aes(contribution, reorder(variable, contribution))) +
geom_point() +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, size = 3, color = "white") +
facet_wrap(~ label, scales = "free_y", ncol = 1) +
ylab(NULL)

Unfortunately, a major drawback to DALEX’s implementation of these algorithm’s is that they are not parallelized. Consequently, wide data sets become extremely slow. For example, performing the previous three prediction_breakdown functions on this attrition data set with 30 predictors takes about 12 minutes. However, this grows exponentially as more predictors are added. When we apply a single instance of prediction_breakdown to the Ames housing data (80 predictors), it took over 3 hours to execute!
# ames data
ames.h2o <- as.h2o(AmesHousing::make_ames())
# create local observation
local_ob <- as.data.frame(ames.h2o[1, ])
# variable names for resonse & features
y <- "Sale_Price"
x <- setdiff(names(ames.h2o), y)
# random forest model
rf <- h2o.randomForest(
x = x,
y = y,
training_frame = ames.h2o,
ntrees = 1000
)
# get features for explainer
x_valid <- as.data.frame(ames.h2o)[, x]
y_valid <- as.vector(ames.h2o[y])
# create custom predict function
pred <- function(model, newdata) {
results <- as.vector(predict(model, as.h2o(newdata)))
return(results)
}
# create explainer
ames_rf <- explain(
model = rf,
data = x_valid,
y = y_valid,
predict_function = pred,
label = "ames"
)
# time to compute prediction break down
system.time({
ames_example <- prediction_breakdown(ames_rf, observation = local_ob)
})
## user system elapsed
## 1518.888 58.439 12188.683
Looking at the underlying code for the prediction_breakdown function (it simply calls breakDown::broken.default), there are opportunities for integrating parallelization capabilities (i.e. via foreach package). Consequently, prior to adding it to your preferred ML toolkit, you should determine:
The following provides resources to learn more about the DALEX package:
DALEX GitHub repo: https://github.com/pbiecek/DALEXbreakDown package which is called by DALEX: https://github.com/pbiecek/breakDownThis tutorial was built with the following packages and R version. All code was executed on 2013 MacBook Pro with a 2.4 GHz Intel Core i5 processor, 8 GB of memory, 1600MHz speed, and double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR3).
# packages used
pkgs <- c(
"rsample",
"dplyr",
"ggplot2",
"h2o",
"DALEX"
)
# package & session info
devtools::session_info(pkgs)
## setting value
## version R version 3.5.0 (2018-04-23)
## system x86_64, darwin15.6.0
## ui X11
## language (EN)
## collate en_US.UTF-8
## tz America/New_York
## date 2018-07-11
##
## package * version date source
## abind 1.4-5 2016-07-21 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## agricolae 1.2-8 2017-09-12 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ALEPlot 1.1 2018-05-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## AlgDesign 1.1-7.3 2014-10-15 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## assertthat 0.2.0 2017-04-11 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## BH 1.66.0-1 2018-02-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## bindr 0.1.1 2018-03-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## bindrcpp * 0.2.2 2018-03-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## bitops 1.0-6 2013-08-17 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## boot 1.3-20 2017-08-06 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## breakDown 0.1.6 2018-06-14 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## broom * 0.4.4 2018-03-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## class 7.3-14 2015-08-30 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## classInt 0.2-3 2018-04-16 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## cli 1.0.0 2017-11-05 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## cluster 2.0.7-1 2018-04-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## coda 0.19-1 2016-12-08 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## colorRamps 2.3 2012-10-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## colorspace 1.3-2 2016-12-14 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## combinat 0.0-8 2012-10-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## compiler 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## cowplot 0.9.2 2017-12-17 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## crayon 1.3.4 2017-09-16 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## CVST 0.2-2 2018-05-26 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## DALEX * 0.2.3 2018-06-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ddalpha 1.3.3 2018-04-30 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## deldir 0.1-15 2018-04-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## DEoptimR 1.0-8 2016-11-19 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## dichromat 2.0-0 2013-01-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## digest 0.6.15 2018-01-28 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## dimRed 0.1.0 2017-05-04 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## dplyr * 0.7.5 2018-05-19 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## DRR 0.0.3 2018-01-06 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## e1071 1.6-8 2017-02-02 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## evaluate 0.10.1 2017-06-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## expm 0.999-2 2017-03-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## factorMerger 0.3.6 2018-04-04 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## forcats 0.3.0 2018-02-19 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## foreign 0.8-70 2017-11-28 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## formula.tools 1.7.1 2018-03-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## gdata 2.18.0 2017-06-06 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## geometry 0.3-6 2015-09-09 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ggplot2 * 2.2.1 2016-12-30 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ggpubr 0.1.6 2017-11-14 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ggrepel 0.8.0 2018-05-09 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ggsci 2.9 2018-05-14 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ggsignif 0.4.0 2017-08-03 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## glue 1.2.0.9000 2018-07-04 Github (tidyverse/glue@a2c0f8b)
## gmodels 2.18.1 2018-06-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## gower 0.1.2 2017-02-23 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## graphics * 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## grDevices * 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## grid 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## gridExtra 2.3 2017-09-09 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## gtable 0.2.0 2016-02-26 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## gtools 3.5.0 2015-05-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## h2o * 3.18.0.11 2018-05-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## haven 1.1.1 2018-01-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## highr 0.6 2016-05-09 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## hms 0.4.2 2018-03-10 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## htmltools 0.3.6 2017-04-28 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## httpuv 1.4.3 2018-05-10 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## ipred 0.9-6 2017-03-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## jsonlite 1.5 2017-06-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## kernlab 0.9-26 2018-04-30 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## KernSmooth 2.23-15 2015-06-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## klaR 0.6-14 2018-03-19 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## knitr 1.20 2018-02-20 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## labeling 0.3 2014-08-23 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## labelled 1.1.0 2018-05-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## later 0.7.2 2018-05-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## lattice 0.20-35 2017-03-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## lava 1.6.1 2018-03-28 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## lazyeval 0.2.1 2017-10-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## LearnBayes 2.15.1 2018-03-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## lubridate 1.7.4 2018-04-11 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## magic 1.5-8 2018-01-26 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## magrittr 1.5 2014-11-22 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## markdown 0.8 2017-04-20 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## MASS 7.3-49 2018-02-23 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## Matrix 1.2-14 2018-04-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## methods * 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## mgcv 1.8-23 2018-01-21 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## mime 0.5 2016-07-07 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## miniUI 0.1.1.1 2018-05-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## mnormt 1.5-5 2016-10-15 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## munsell 0.4.3 2016-02-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## mvtnorm 1.0-8 2018-05-31 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## nlme 3.1-137 2018-04-07 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## nnet 7.3-12 2016-02-02 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## numDeriv 2016.8-1 2016-08-27 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## operator.tools 1.6.3 2017-02-28 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## parallel 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## pdp 0.6.0 2017-07-20 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## pillar 1.2.3 2018-05-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## pkgconfig 2.0.1 2017-03-21 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## plogr 0.2.0 2018-03-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## plyr 1.8.4 2016-06-08 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## prodlim 2018.04.18 2018-04-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## promises 1.0.1 2018-04-13 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## proxy 0.4-22 2018-04-08 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## psych 1.8.4 2018-05-06 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## purrr 0.2.5 2018-05-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## questionr 0.6.2 2017-11-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## R6 2.2.2 2017-06-17 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## RColorBrewer 1.1-2 2014-12-07 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## Rcpp 0.12.17 2018-05-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## RcppRoll 0.2.2 2015-04-05 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## RCurl 1.95-4.10 2018-01-04 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## readr 1.1.1 2017-05-16 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## recipes 0.1.2 2018-01-11 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## reshape2 1.4.3 2017-12-11 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## rlang 0.2.1 2018-05-30 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## robustbase 0.93-0 2018-04-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## rpart 4.1-13 2018-02-23 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## rsample * 0.0.2 2017-11-12 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## rstudioapi 0.7 2017-09-07 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## scales 0.5.0 2017-08-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## sfsmisc 1.1-2 2018-03-05 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## shiny 1.1.0 2018-05-17 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## sourcetools 0.1.7 2018-04-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## sp 1.2-7 2018-01-19 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## spData 0.2.8.3 2018-03-25 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## spdep 0.7-7 2018-04-03 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## splines 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## SQUAREM 2017.10-1 2017-10-07 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## stats * 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## stringi 1.2.2 2018-05-02 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## stringr 1.3.1 2018-05-10 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## survival 2.41-3 2017-04-04 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## tibble 1.4.2 2018-01-22 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## tidyr * 0.8.1 2018-05-18 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## tidyselect 0.2.4 2018-02-26 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## timeDate 3043.102 2018-02-21 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## tools 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## utf8 1.1.4 2018-05-24 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## utils * 3.5.0 2018-04-24 local
## viridis 0.5.1 2018-03-29 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## viridisLite 0.3.0 2018-02-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## xtable 1.8-2 2016-02-05 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## yaImpute 1.0-29 2017-12-10 CRAN (R 3.5.0)
## yaml 2.1.19 2018-05-01 CRAN (R 3.5.0)